HSP-90 Inhibitors as a Senolytic and Anti-Aging Molecule
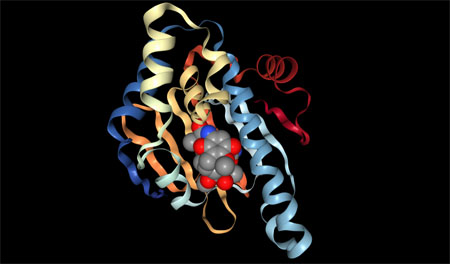
HSP-90 Molecule --GELDANAMYCIN BOUND TO THE HSP90 GELDANAMYCIN-BINDING DOMAINPDB: 1YET
18 April 1997 --Crystal structure of an Hsp90-geldanamycin complex: targeting of a protein chaperone by an antitumor agent.
The Hsp90 chaperone is required for the activation of several families of eukaryotic protein kinases and nuclear hormone receptors, many of which are protooncogenic and play a prominent role in cancer. The geldanamycin antibiotic has antiproliferative and antitumor effects, as it binds to Hsp90, inhibits the Hsp90-mediated conformational maturation/refolding reaction, and results in the degradation of Hsp90 substrates. The structure of the geldanamycin-binding domain of Hsp90 (residues 9-232) reveals a pronounced pocket, 15 A deep, that is highly conserved across species. Geldanamycin binds inside this pocket, adopting a compact structure similar to that of a polypeptide chain in a turn conformation. This, and the pocket's similarity to substrate-binding sites, suggest that the pocket binds a portion of the polypeptide substrate and participates in the conformational maturation/refolding reaction. see full publication
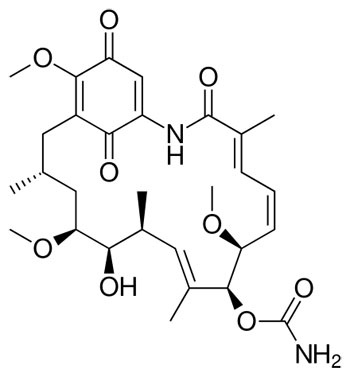
Geldanamycin Molecular Structure
Geldanamycin is a 1,4-benzoquinone ansamycin antitumor antibiotic that inhibits the function of Hsp90 (Heat Shock Protein 90) by binding to the unusual ADP/ATP-binding pocket of the protein. HSP90 client proteins play important roles in the regulation of the cell cycle, cell growth, cell survival, apoptosis, angiogenesis and oncogenesis.ABSTRACTS
23 July 2018 --Hsp90 inhibitors as senolytic drugs to extend healthy aging
"...Aging is characterized by progressive decay of biological systems and although it is not considered a disease, it is one of the main risk factors for chronic diseases and many types of cancers. The accumulation of senescent cells in various tissues is thought to be a major factor contributing to aging and age-related diseases. Removal of senescent cells during aging by either genetic or therapeutic methods have led to an improvement of several age related disease in mice. In this preview, we highlight the significance of developing senotherapeutic approaches to specifically kill senescent cells (senolytics) or suppress the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) that drives sterile inflammation (senomorphics) associated with aging to extend healthspan and potentially lifespan. Also, we provide an overview of the senotherapeutic drugs identified to date. In particular, we discuss and expand upon the recent identification of inhibitors of the HSP90 co-chaperone as a new class of senolytics. KEYWORDS: Aging, cell senescence, apoptosis, DNA damage, Mitochondria...
...HSPs are considered as overall stress response proteins that stabilize unfolded or misfolded proteins, giving the cell time to repair damaged proteins under stressful conditions such as heat shock, pH shift, heavy metals or hypoxia [22–24] . The increase in the level of HSPs is regulated at the transcriptional level by HSF1 (heat shock factor 1), one of the main transcription factors induced in response to proteotoxic cell stress [25,26]. HSPs are conveniently named after their molecular size (HSP60, HSP70, HSP90) in kDa and are generally ATP dependent [27,28]..." see full publications and references therein
04 September 2017 -- Identification of HSP90 inhibitors as a novel class of senolytics
Aging is the main risk factor for many chronic degenerative diseases and cancer. Increased senescent cell burden in various tissues is a major contributor to aging and age-related diseases. Recently, a new class of drugs termed senolytics were demonstrated to extending healthspan, reducing frailty and improving stem cell function in multiple murine models of aging. To identify novel and more optimal senotherapeutic drugs and combinations, we established a senescence associated β-galactosidase assay as a screening platform to rapidly identify drugs that specifically affect senescent cells. We used primary Ercc1 −/− murine embryonic fibroblasts with reduced DNA repair capacity, which senesce rapidly if grown at atmospheric oxygen. This platform was used to screen a small library of compounds that regulate autophagy, identifying two inhibitors of the HSP90 chaperone family as having significant senolytic activity in mouse and human cells. Treatment of Ercc1 −/∆ mice, a mouse model of a human progeroid syndrome, with the HSP90 inhibitor 17-DMAG extended healthspan, delayed the onset of several age-related symptoms and reduced p16INK4a expression. These results demonstrate the utility of our screening platform to identify senotherapeutic agents as well as identified HSP90 inhibitors as a promising new class of senolytic drugs.... see full publication
Anti-Aging and Senolytics Home Page
- What is Anti-Aging Medicine
- What is Senescence?
- What are Senolytics?
- About Caloric Restriction
- Mtor and Rapamycin
- The IKK/NF-κB signaling pathway in aging
- Exercise and Anti-Aging
- Meditation and Anti-Aging
SENOLYTIC AND ANTI-AGING MOLECULES
RAPAMYCIN ---The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway has a central role in cell activation...
METFORMIN -- The diabetes drug metformin used by some for anti-aging may diminish benefits of aerobic exercise...
QUERCETIN-- AND WITH DASATINIB--The senolytic cocktail, dasatinib plus quercetin, which causes selective elimination of senescent cells...
FISETIN--Of the 10 flavonoids tested, fisetin was the most potent senolytic...
EGCG- The most active component of green tea....
NAD BOOSTERS --'...The cells of the old mice were indistinguishable from the young mice, after just one week of treatment...
SULFORAPHANE-- An isothiocyanate present in cruciferous vegetables activates antioxidant and anti-inflammatory responses by ...
UROLITHIN --Metabolite of Pomegranate compound with anti-aging effects passes human trial...
MITO-Q -- A water soluble fomr of CoQ10 that has excellent absorption and high bioavailability...
HONOKIOL - A bioactive natural product derived from Magnolia Bark have demonstrated ...
CURCUMIN AND ANALOGS -Recent research is focused on the design and synthesis of curcumin analogs as antiproliferative and anti-inflammatory agents...
BERBERINE --berberine has recently been reported to expand life span in Drosophila melanogaster, and attenuate premature cellular senescence
N-ACETYL-CYSTINE (NAC)--"...pretreatment with NAC increased glutathione levels in the older cells and largely helped offset that level of cell death..."
PIPERLONGUMINE - A natural product from the Long pepper with high bioavailability...
RESVERATROL AND PTEROTSILBINE -- Pterostilben chemically similar to resveratrol bute differs from resveratrol by exhibiting increased bioavailability (80% compared to 20% in resveratrol)
SPERMIDINE--Spermidine delays aging in humans ...
ALLICIN -- Allicin is a compound produced when garlic is crushed or chopped. ...
VITAMIN D3 -- Production of the active forms of Vitamin D are reduced by 50% as a result of an age-related decline
VITAMIN K-- evidence suggests vitamin K has an anti-inflammatory action
TOCOTRIENOL(AND WITH QUERCETIN) --Tocotrieniols have been found to exert a synergistic antitumor effect on cancer cells when given in combination....
HSP-90 INHIBITORS --As a novel class of senolytics
The Cannabidiol Molecule
Cannabidiol (CBD is the major non-psychoactive component of Cannabis and is being looked at by major drug and consumer companies for various medical and social uses.