South African Variant --The E484K, N501Y, K417N Mutation
B.1.351 lineage (a.k.a. 20H/501Y.V2)
- This variant has multiple mutations in the spike protein, including K417N, E484K, N501Y. Unlike the B.1.1.7 lineage detected in the UK, this variant does not contain the deletion at 69/70.
- This variant was first identified in Nelson Mandela Bay, South Africa, in samples dating back to the beginning of October 2020, and cases have since been detected outside of South Africa, including the United States
- The variant also was identified in Zambia in late December 2020, at which time it appeared to be the predominant variant in the country.
- Currently there is no evidence to suggest that this variant has any impact on disease severity.
- There is some evidence to indicate that one of the spike protein mutations, E484K, may affect neutralization by some polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies. source: cdc.gov
The E484K mutation occurs in the receptor-binding domain (RBD) that the virus uses to bind to the human ACE2 receptor and has been associated with escape from neutralizing antibodies.
Risk of the E484K -- Is E484K
There has been research showing that the current vaccines work against the UK B.1.1.7 variant without the E484K mutation. However, recent clinical trials by Novavax and Johnson & Johnson showed that their new vaccines were less effective in South Africa compared with the UK or US, which is presumably because of the high level of virus carrying the E484K mutation. see: Covid-19: The E484K mutation and the risks it poses
Perhaps the biggest problem is that the E484 is the site in the RBD where mutations usually have the largest effect on binding and neutralization. source
The cause of antibody neutralization is most likely the result of conformational change of the spike protein
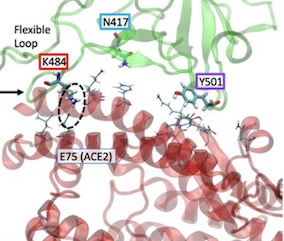
E484K shows increased contact with hACE2 E75 ----E484K, whether in the presence of both K417N, and N501Y variants or as the only variant in the presence of K417 and N501 is associated with increased contact between RBD residue 484 and ACE2 E75 (Figures 1a-d)
As shown in Figure 1a below, the E484K, K417N, and N501Y mutants span the S RBD-ACE2 interface, with the E484K substitution occurring in a highly flexible loop region of the S RBD (Fig. 1c). The N501Y substitution is found in a second region of contact11, and the K417N mutation in a region between the two that shows relatively little interaction with ACE2.
From Nelson et al., ABSTRACT "...We report here the combination of E484K, K417N and N501Y results in the highest degree of conformational alterations of S RBD when bound to hACE2, compared to either E484K or N501Y alone. Both E484K and N501Y increase affinity of S RBD for hACE2 and E484K in particular switches the charge on the flexible loop region of RBD which leads to the formation of novel favorable contacts. Enhanced affinity of S RBD for hACE2 very likely underpins the greater transmissibility conferred by the presence of either E484K or N501Y; while the induction of conformational changes may provide an explanation for evidence that the 501Y.V2 variant, distinguished from the B.1.1.7 UK variant by the presence of E484K, is able to escape neutralization by existing first-wave anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and re-infect COVID-19 convalescent individuals....
...We report here the combination of E484K, K417N and N501Y results in the highest degree of conformational alterations of S RBD when bound to hACE2, compared to either E484K or N501Y alone. Both E484K and N501Y increase affinity of S RBD for hACE2 and E484K in particular switches the charge on the flexible loop region of RBD which leads to the formation of novel favorable contacts. Enhanced affinity of S RBD for hACE2 very likely underpins the greater transmissibility conferred by the presence of either E484K or N501Y; while the induction of conformational changes may provide an explanation for evidence that the 501Y.V2 variant, distinguished from the B.1.1.7 UK variant by the presence of E484K, is able to escape neutralization by existing first-wave anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies and re-infect COVID-19 convalescent individuals...."
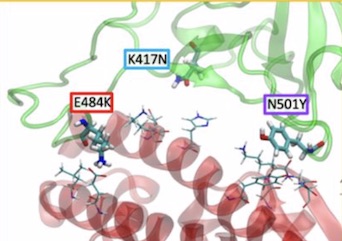
Fig 1a- Nelson et al., The K484 substitution in the novel South African variant increases affinity of the spike receptor binding domain (S RBD) for ACE2. The positions of the E484K (red), K417N (cyan), and N501K (purple) substitutions at the interface of the 501Y.V2 variant S RBD - hACE2 interface are shown. hACE2 residues nearest to the mutated RBD residues are rendered as thin sticks. The E484K mutation is located in a highly flexible loop region of the interface, K417N in a region with lower probability of contact, and N501K at a second point of high-affinity contact.
Additional support for the threat posed by mutations at residue 484 is provided by Greaney et al., who undertook an impressive effort to map mutations that affect binding of ten human monoclonal antibodies. By employing a deep mutational scanning method, they found that mutations at residue 484 have a high probability of affecting antibody binding.
-------------->spin on -------->- spin off
-------------->zoom into receptor binding site
-(Amino acids K417, E484, N501)
------->- zoom out
Jmol Menu --->>Right-Click
-------------->spin on -------->- spin off
-------------->zoom into receptor binding site
-(Amino acids E75, N417, K484, Y501)
------->- zoom out
Jmol Menu --->>Right-Click
Vaccine Efficacy against African Strain
The E484K and N501Y variants and VaccinesNeutralization of SARS-CoV-2 spike 69/70 deletion, E484K and N501Y variants by BNT162b2 vaccine-elicited sera --"...Neutralization geometric mean titers (GMTs) of 20 BTN162b2 vaccine-elicited human sera against the three mutant viruses were 0.81- to 1.46-fold of the GMTs against parental virus, indicating small effects of these mutations on neutralization by sera elicited by two BNT162b2 doses. .."
The E484K mutation in the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein reduces but does not abolish neutralizing activity of human convalescent and post-vaccination sera -- "...human sera with high neutralization titers against the USA-WA1/2020 strain were still able to neutralize the E484K rSARS-CoV-2. Therefore, it is important to aim for the highest titers possible induced by vaccination to enhance protection against newly emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants. Two vaccine doses may be needed for induction of high antibody titers against SARS-CoV-2. ..."
Sars-CoV-2 Variants
The novel coronavirus SARS-CoV2
B.1.1.7 and B.1.525 UK variant
B.1.427/B.1.429, California QP77P Mutation
B.1.526, NY E484K or S477N Mutations
Molecules of Disease
-
Small Molecules
Cholesterol
Nicotine
Trans Fatty Acid
Alcohol
Acetyaldehyde
- Proteins
Cytokines
Hemoglobin S
Prions
Botulinum Toxin
Explain it with Molecules
- Why is water such a good solvent?
- Why does ice float?
- Why do solids, liquids and gases behave differently?
- What is the geometry of methane?
- What's the difference between alpha and beta glucose?
- How does caffeine work in the brain?
- How does soap work?
- What is the difference between sucrose and fructose?
- Why is carbon monoxide so dangerous?
- Why is graphite so soft if it is made of only carbon?
- What is the difference between Carbyne and Graphite?
- Why is the fullerene and similar structures the cornerstone of nanotechnology?
- How big is a nanotube?
- Why does table salt have a cubic crystal shape?
- What is the structure of the benzene molecule?
- Why do carcinogens cause cancer?
- What causes Sickle Cell Anemia?
- What is the difference between sodium nitrite and nitrate?
- How do drugs work?